- Consortium: Nommon (project coordinator) and Populus.
- 2021 – 2022
- ai4cities.eu

The project
AVENUE aimed at developing an AI-based decision support tool for designing and monitoring shared mobility regulatory frameworks oriented towards the reduction of GHG emissions. The project was part of AI4Cities, a three-year EU-funded programme that brought together leading European cities looking for artificial intelligence (AI) solutions to accelerate carbon neutrality. Nommon and Populus joined forces to present AVENUE, a proposal in response to the mobility challenge.
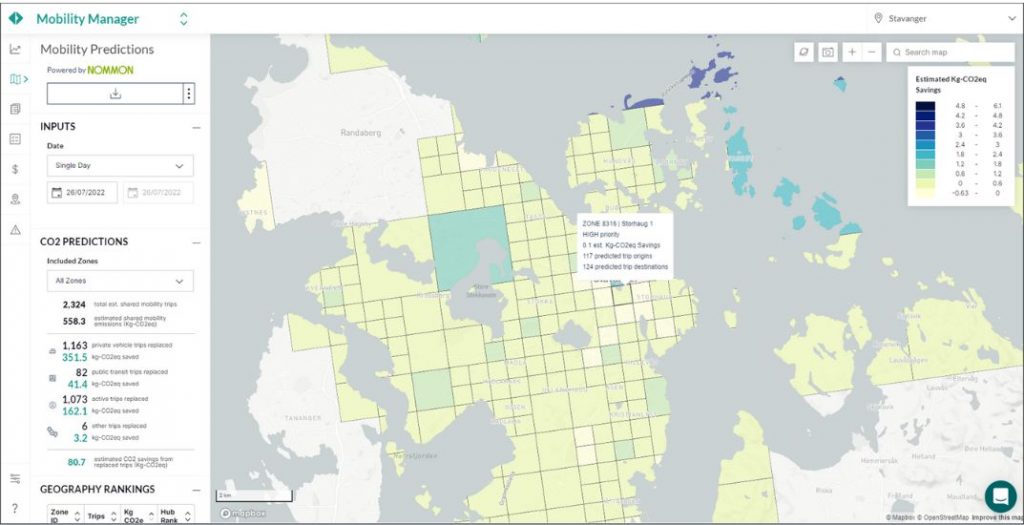
The project exploited the information provided by two existing solutions for collecting and leveraging geolocated big data: Populus’ Mobility Manager, which enables cities to gather, aggregate and analyse the data that mobility operators share with authorities to manage the enforcement of regulatory measures, and Nommon Mobility Insights, which processes the registers from mobile network data and other geolocated sources to provide actionable insights about people’s activity and mobility patterns. The combination of this information with other data sources available by cities was used to develop demand prediction models capable of simulating the modal choice process around shared mobility services and the way these modal choices can be influenced by different regulatory strategies. The outcome of these models served to evaluate the carbon footprint effects of different possible measures.
Goals
The main goal of AVENUE was to develop an AI-based solution capable of evaluating how shared mobility services contribute to GHG emission reduction and help policy making processes through evidence-based inputs rather than prescribing rigid solutions.
The specific objectives of the project were the following:
- Define the needs that transport authorities have regarding shared mobility and CO2 in order to include the necessary indicators and functionalities in the platform.
- Formulate, calibrate and validate demand models for shared mobility systems that predict not only the demand, but also the CO2 emissions as well as the modal shift it implies.
- Develop simulation tools that allow authorities to assess the impact on the sustainability of mobility in the city as a whole for different regulatory scenarios of shared mobility services.
- Integrate the developed models into a decision support system equipped with an API and a visualisation dashboard that allow users to evaluate decisions regarding shared mobility.
Project phases
Phase 1: Solution Design
Nommon and Populus worked together in the AI4Cities’s Solution Design Phase. Both companies worked for three months on the design of the AVENUE solution, analysing the cities’ needs related to GHG emissions and shared mobility systems, and evaluated the different data sources available to feed the solution’s model.
Phase 2: Prototyping
AVENUE was selected to move forward to AI4Cities’ phase 2 to create the first prototype of the solution proposed in Phase 1. Nommon and Populus’ teams continued working on the development of the prototype until January 2022.
Phase 3: Piloting
AVENUE was selected to proceed to Phase 3 of the project. The solution was piloted in two of the participant cities: Stavanger and Tallinn. This opportunity allowed the consortium to refine the functionalities of the tool and add new ones to enable cities to more efficiently plan and manage shared mobility systems. In addition to the reduction of emissions indicators, Nommon and Populus worked on different use cases that allowed, for example, the location of mobility hubs, the expansion of the shared mobility system, or the optimisation of no-parking zones. In this phase the tool was tested in real conditions by end users, which provided AVENUE valuable insights.
Results
AVENUE developed an interactive visualisation tool to facilitate long-term decision-making processes related to the implementation of smart mobility systems from a climate change mitigation perspective. However, the tool’s functionalities also provide other benefits related to different areas of sustainability that extend beyond the reduction of GHG emissions. For instance, policies addressing the carbon footprint of shared mobility services are likely to have a positive impact on other environmental aspects, such as energy consumption and air quality. Additionally, gaining a better understanding of the patterns of choice of transport modes open the door to more detailed analyses of the social sustainability of smart mobility. This includes considering factors like age, gender, or income that influence the use and accessibility of these modes and their effects on the most vulnerable users.
The work carried during the project helped us evolve our solution WiseRide to better serve policymakers and shared mobility operators in harnessing the potential of these services. AVENUE facilitated close collaboration with relevant stakeholders and enabled us to enhance our solution so it better contributes to improve the planning and monitoring of shared mobility services, to optimise the resources used by the authorities, and to facilitate collaboration between shared mobility and public transport.

AVENUE is part of the AI4Cities project that has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme.
